Design for High Availability – WAN Availability and QoS
2 min read
Most businesses need a high level of availability, especially for their critical applications. The goal of high availability is to remove the single points of failure in the network design by using software features or hardware-based resiliency. Redundancy is critical in providing high levels of availability for the enterprise. Some technologies have built-in techniques that enable them to be highly available. For technologies that do not have high availability, other techniques can be used, such as additional WAN circuits or backup power supplies.
Defining Availability
System availability is a ratio of the expected uptime to the amount of downtime over the same period of time. Let’s take an example of 4 hours of downtime per year. There are 365 days in a year, which equals 8760 hours (365 × 24 = 8760). Now, if we subtract 4 hours from the annual total of 8760 hours, we get 8756. Then, if we figure 8756 / 8760 × 100, we get the amount of availability percentage, which in this case is 99.95%.
Table 9-5 shows the availability percentages from 99% to 99.999999%, along with amounts of downtime per year.
Table 9-5 Availability Percentages
| Availability | Downtime per Year | The Nines of Availability | Targets |
| 99.000000% | 3.65 days | Two nines | |
| 99.900000% | 8.76 hours | Three nines | |
| 99.990000% | 52.56 minutes | Four nines | Branch WAN high availability |
| 99.999000% | 5.256 minutes | Five nines | Branch WAN high availability |
| 99.999900% | 31.536 seconds | Six nines | Ultra high availability |
| 99.999990% | 3.1536 seconds | Seven nines | Ultra high availability |
| 99.999999% | .31536 seconds | Eight nines | Ultra high availability |
Figure 9-1 illustrates WAN router paths and the impacts to availability depending on the level of redundancy used.
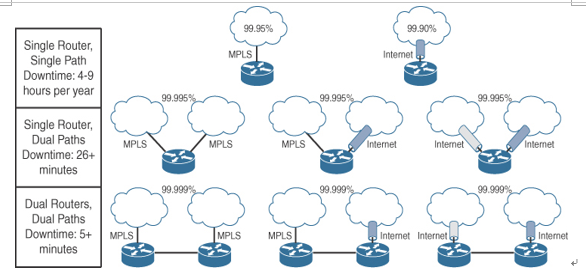
Figure 9-1 Router Paths and Availability Examples
Deployment Models
There are three common deployment models for WAN connectivity, each with pros and cons:
- MPLS WAN: Single- or dual-router MPLS VPN
- Hybrid WAN: MPLS VPN and Internet VPN
- Internet WAN: Single- or dual-router Internet VPN
An MPLS WAN involves single or dual routers for the MPLS VPN connections. It provides for the highest in SLA guarantees for both QoS capabilities and network availability. However, this option is the most expensive, and it ties the organization to the service provider. New cloud-based designs are using MPLS Direct Connect to provide connectivity to AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
A hybrid WAN combines an MPLS VPN and an Internet VPN on a single router or on a pair of routers. This deployment model offers a balanced cost option between the higher-cost MPLS VPN connection and the lower-cost Internet VPN for backup. With a hybrid WAN, traffic can be split between the MPLS VPN for higher-priority-based traffic and Internet VPN for lower-priority-based traffic. Newer WAN designs are also using SDWAN with both MPLS and Internet-based transports.
An Internet WAN includes a single router or dual routers using Internet-based VPN only. These can also include cloud solutions for connectivity to AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This deployment model is the lowest-cost option but lacks the SLAs and QoS capabilities offered by carriers. The enterprise would be responsible for providing SLAs to the end users.




