Metro Ethernet – WAN for the Enterprise
2 min read
Demand for bandwidth in metropolitan-area networks (MANs) is increasing due to the high throughput requirements of data-intensive applications. Today, many SPs are offering Metro Ethernet services to fulfill the demand; these offerings are based on Ethernet, IP, and optical technologies such as dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) or coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM).
Metro Ethernet uses Ethernet to deliver low-cost and high-speed MAN/WAN connectivity for organizations. Many service providers now offer Metro Ethernet solutions to deliver a wide range of converged network services, such as data, voice, and video, on the same wire. Metro Ethernet provides enterprise LAN type functionality out in the MAN and WAN, increasing the throughput available for applications. Metro Ethernet bandwidths can range from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps (and even higher in some cases), supporting higher performance and increased QoS requirements. In contrast to the rigid nature of traditional circuit provisioning, Metro Ethernet services are much easier to deploy and scale due to the flexible bandwidth increments. Metro Ethernet technology is appealing to many customers who are already comfortable using Ethernet throughout their LAN environments.
Table 8-3 shows the benefits that Ethernet handoffs at the customer edge provide.
Table 8-3 Benefits of Ethernet Handoffs at the Customer Edge
| Benefit | Description |
| Service-enabling solution | Layering value-added services in addition to the network |
| Flexible architecture | No need for a truck roll for increasing port speeds No need for new customer premises equipment (CPE) Evolving existing WAN services to an IP-based solution |
| Seamless enterprise integration | Ease of integration with existing LAN network equipment |
SONET/SDH
SONET/SDH is circuit based and delivers high-speed services over an optical network. SONET is defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) specification, and the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) defines SDH. SONET/SDH guarantees bandwidth and has line rates of 155 Mbps to more than 10 Gbps. Common circuit sizes are OC-3, or 155 Mbps, and OC-12, or 622 Mbps.
SONET/SDH uses a ring topology to connect sites and provide automatic recovery capabilities, and it has self-healing mechanisms. SONET/SDH rings support ATM or POS IP encapsulations. The Optical Carrier (OC) rates are the digital bandwidth hierarchies that are part of the SONET/SDH standards. The Optical Carrier speeds supported are as follows:
- OC-1 = 51.85 Mbps
- OC-3 = 155.52 Mbps
- OC-12 = 622.08 Mbps
- OC-24 = 1.244 Gbps
- OC-48 = 2.488 Gbps
- OC-192 = 9.952 Gbps
- OC-255 = 13.21 Gbps
Figure 8-4 shows an OC-48 SONET ring with connections to three sites that share the ring.
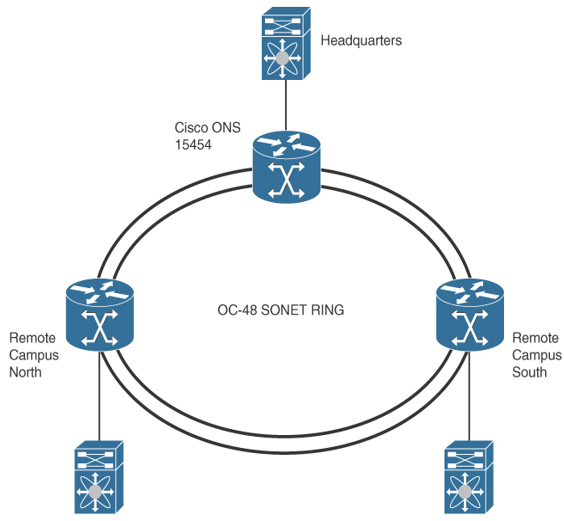
Figure 8-4 SONET/SDH




