Multi-Homed MPLS WANs – WAN Availability and QoS
2 min read
In a dual-MPLS-carrier design, each site is connected to both provider A and provider B. Some sites might have two routers for high availability, and others might have only a single router but with two links for link and provider redundancy. For example, each CE router would redistribute local routes from EIGRP into BGP. Routes from other sites would be redistributed from BGP into EIGRP as external routes. For sites that have two routers, filtering or tagging of the routes in and out of BGP would be needed to prevent routing loops.
Figure 9-3 illustrates a dual-MPLS-carrier design with single and dual routers.
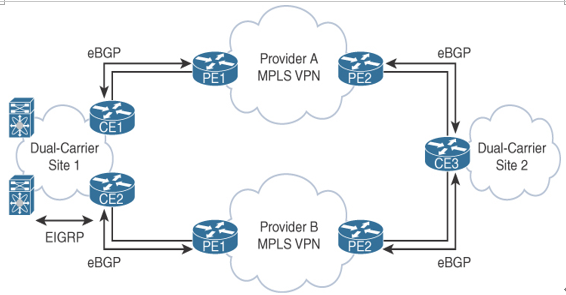
Figure 9-3 Dual-MPLS-Carrier Design Example
Hybrid WANs: Layer 3 VPN with Internet Tunnels
Hybrid WAN designs involve using an MPLS VPN for the primary connection and an Internet tunnel for the backup connection. In this design, eBGP would be used to peer with the MPLS VPN provider, and EIGRP would be used for routing for the IGP internally. At each site, the CE router would learn routes from the MPLS VPN via BGP and redistribute the routes from BGP into EIGRP. Then each site would redistribute EIGRP routes into BGP and use EIGRP to peer with other local routers at each site. The Internet tunnel routers would use EIGRP to exchange routes inside the VPN tunnels, and they would not need to redistribute routing information because they would run only EIGRP. On the MPLS VPN router, BGP-learned routes would be preferred because the BGP routes that would be redistributed into EIGRP routes would have a lower administrative distance. In this case, if you want the MPLS VPN router to be the primary path, you need to run an FHRP between the dual-homed routers, with the active router being the MPLS VPN-connected router. That way, it would choose the MPLS VPN path as the primary path and use the Internet tunnel path as the backup path for failover. Another option would be to modify the routing protocol metrics so that the MPLS VPN path is preferred. Another hybrid design approach is WAN integration that can be used to provide high availability for cloud connectivity with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
WAN integration is a service that provides seamless connectivity between a customer’s on-premises hosted data center and a cloud provider’s data center. This service is delivered through a hybrid WAN architecture that combines MPLS and Internet connections. WAN integration allows for improved application performance, optimized traffic routing, and reduced costs compared to dedicated MPLS connections.
Figure 9-4 illustrates a hybrid WAN design with an MPLS VPN and an Internet VPN.
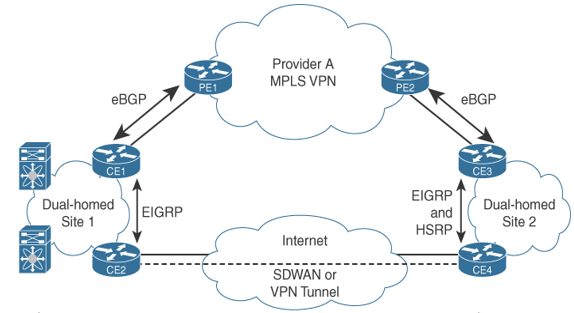
Figure 9-4 Hybrid WAN Design Example




