SD-WAN Customer Edge – WAN for the Enterprise
2 min read
Software-defined networking is a centralized approach to managing a network that abstracts away the underlying network infrastructure from its applications. SD-WAN is part of the overall SDN paradigm. The Cisco SD-WAN solution is an enterprise-class WAN architecture overlay that fully integrates routing, security, orchestration, and centralized policy into next-generation networks. Cisco SD-WAN is transport independent and allows for a mix of transports, including MPLS, 4G/5G, and low-cost Internet links in many combinations that extend to the data center, branch, and cloud. In addition, Cisco SD-WAN’s integration with Megaport provides on-demand branch connectivity with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, directly from your SD-WAN controller.
The Cisco SD-WAN solution separates functions into four planes for operation:
- Control: The control plane builds and maintains the network topology and informs the data plane about where traffic flows using the vSmart controller.
- Data: The data plane is responsible for forwarding packets with instructions from the control plane through the vEdge router, which can be physical or virtual.
- Management: The management plane is responsible for centralized management and monitoring through the use of vManage.
- Orchestration: The orchestration plane helps with the onboarding of the SD-WAN routers into the SD-WAN overlay using the vBond orchestrator.
Figure 8-8 provides an overview of the Cisco SD-WAN solution.
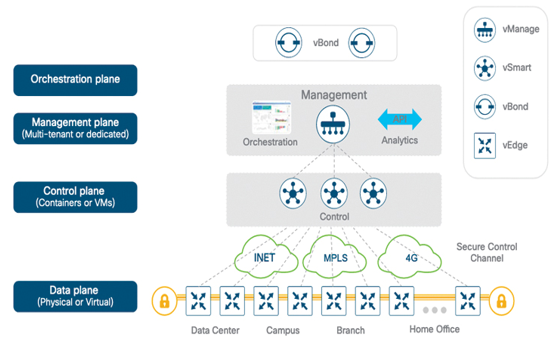
Figure 8-8 Overview of a Cisco SD-WAN Solution
The SD-WAN customer edge platform options for the data plane or vEdge consist of physical or software devices. There are physical device options consisting of branch services routers or vEdge appliances. For the software devices, you have three different options of vEdge cloud devices. Depending on the requirements for your data center, campus, and branch or home office vEdge solution, there are several options with various speed and WAN transport characteristics. Table 8-4 lists the SD-WAN physical and software device options.
Table 8-4 SD-WAN Platform Options
| Physical Devices | Software Devices | |||
| Branch Services/Data Center | vEdge Appliances for Branch/Data Center | Universal CPE | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
| ISR 1000 200 Mbps | vEdge 100 100 Mbps | ENCS 5100 vEdgeCloud: ISRv Up to 250 Mbps | OpenStack vEdgeCloud: CSR1000v | Microsoft Azure vEdgeCloud: CSR1000v |
| ISR 4000 Up to 2 Gbps | vEdge 1000 Up to 1 Gbps | ENCS 5400 vEdgeCloud: ISRv 250 Mbps–2 Gbps | ESXi CSR1000v | Amazon Web Services vEdgeCloud: CSR1000v |
| ASR 1000 Fixed 2.5 Gbps and up | vEdge 2000 10 Gbps | KVM CSR1000v | ||
WAN Link Categories
WAN link characteristics generally fall into two broad categories: private and shared. When you’re selecting a WAN technology, there are many factors to consider, such as how the WAN is going to be used, costs, advantages, and what technology options are available in a given area. Table 8-5 identifies various WAN link characteristics.
Table 8-5 WAN Link Characteristics
| Use | Cost | Advantages | Examples | |
| Private | WAN to connect distant LANs | Private equipment Private configuration Expensive to maintain | High security Transmission quality | Metro Ethernet using dark fiber |
| Shared | Shared-circuit or label-switched WAN | Relatively low cost Leased bandwidth Leased or private equipment | Provider maintenance Shared network for multiple sites | MPLS |
There are fixed and recurring costs in most WAN environments. Fixed costs include the network equipment, circuit provisioning, and network management tools. The recurring costs include the service provider monthly WAN service fees, the maintenance costs of the WAN, and the costs of network operations personnel.




