WAN Overview – WAN for the Enterprise
2 min read
WANs provide network connectivity for the enterprise core and remote branch locations. The enterprise edge, on the other hand, securely connects the enterprise core to the Internet in order to provide DMZ-type services such as VPN connectivity and other cloud-related connectivity such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. Many WAN and Internet transport options are available, and new ones are continually emerging. When you are selecting WAN transport technologies, it is important to consider factors such as cost, bandwidth, reliability, and manageability, in addition to the hardware and software capabilities of the equipment. Moreover, enterprise branch offices can take advantage of a shared network such as MPLS WAN or use the Internet for secure VPN connectivity back to the headquarters or main office, which many are using today as a backup to their high-cost WAN circuits.
WAN Defined
Wide-area networks (WANs) are communications networks used to connect geographically disperse network locations. Generally, service providers or telecommunication carriers offer WAN services. WANs can transport data, voice, and video traffic between the locations of a business. Service providers charge fees, called tariffs, for providing WAN services or communications to their customers. The term service is used to refer to the WAN communications provided by a service provider or carrier.
When designing a WAN, you should become familiar with the design’s requirements, which typically derive from these two important goals:
- Service-level agreement (SLA): An SLA defines the availability of the network. Networked applications rely on the underlying network between the client and server to provide their functions. An SLA negotiated with a service provider can include multiple levels of application availability. Organizations have to work with a carrier to define what level of service—including bandwidth, allowed latency, and loss—is acceptable to the organization.
- Cost and usage: To select the correct reliable WAN service, you must consider the budget and usage requirements of the WAN service.
There are three key objectives of an effective WAN design:
- The WAN needs to support the goals and policies of the organization.
- The WAN technologies selected need to meet the current application requirements and provide for growth of the organization in the future.
- The proposed design should incorporate security throughout and ensure high availability where applicable while staying within budget.
Figure 8-1 shows a typical enterprise with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) WAN and Internet connections.
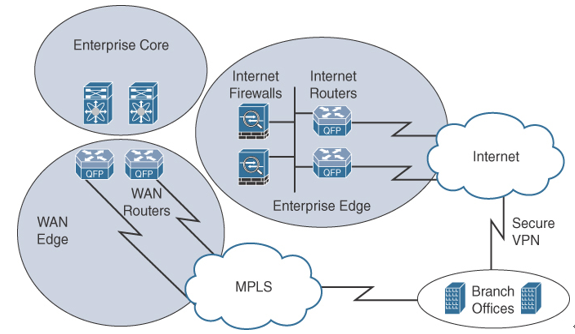
Figure 8-1 WAN and Enterprise Edge




